
 |
aleppoEPOC help is delivered in the form of a database of help topics, as shown in the following example — topic list on right hand side of diagram. Each topic has a title, body text, application name, and some synonyms to aid in topic searching. Aleppo generates help databases from source documents in which each of these fields is identified by style marked paragraphs.
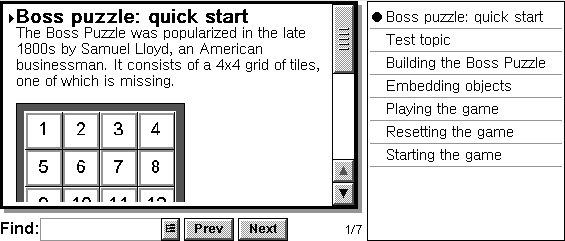
Groups of applications released simultaneously may, optionally, share a help database. This is the method used to provide Help for the standard EPOC applications. The application name can be used to locate all the topics belonging to a specific application. Synonyms provide alternative keywords for locating a topic during a search. For more information on Help file structure see Help database structure.
Aleppo supports various localisation and customisation options that can be used to change the topic order and appearance of the final help database. The following sections explain help file generation in greater detail.
The process of aleppo help authoring is illustrated in the following diagram:
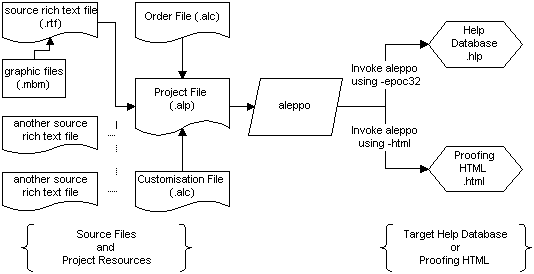
aleppoAleppo is invoked with a single command, that specifies the type of output file to be produced and the name of a project file. The project file, see Project files, defines the location of all project resources needed to generate the help database, including source files, source directories, graphics directories, working directories and output files/directories.
The project file must specify a source rich-text file for every application to be stored in the database. Topic fields in the final database, e.g. topic title, body text, synonyms etc., are represented by style-marked paragraphs in each rich-text file.
The project file may also, optionally, specify the location of an order file and/or a customisation file. These files determine the order of selected topics, and the appearance of text in the final database, respectively.
The process of help authoring is thus:
aleppo e.g. Microsoft Word for Windows documents based on the epochelp.dot templatealeppo to convert to a target formataleppo.In order to use aleppo successfully, it is important to know something about how rich-text files are used in the conversion process. The conversion is based on styled markup. It conveys no formatting information from the rich-text file, except for bold, italic, subscript and superscript, and the style names of paragraphs and characters. It does not convey tabs, hard line breaks (shift+enter), or any other formatting information such as fonts, underline, margin settings, borders etc. This means that character and paragraph styles must be used to convey all formatting information to aleppo.
Aleppo is supplied with a document template for Microsoft Word, which contains all the styles needed for EPOC help authoring.
Section Contents
To create an aleppo rich-text source file using Microsoft Word:
epochelp templateFor more information on the format of aleppo RTF files, see RTF file format.
To create an aleppo project file:
\aleppo\projdir\boss.alpFor more information on the format of aleppo project files, see Project files.
An order file can be created to specify the order that topics appear in the help database. If no order file is defined, topics are displayed alphabetically. For more information on order files, see Order files.
A customisation file can be created to specify the appearance of the help database, including the font used for text, its size, and the appearance of tip, important and note effects. If no customisation file is specified, a default appearance is applied. For more information on customisation files, see Customisation files.
aleppoTo run aleppo,
.alp is not enforced.|
|